Wednesday, 4 November 2020
Friday, 30 October 2020
Monday, 26 October 2020
Career As Geochemist- Pattern ,Syllabus, Strategies & Tricks
GEOCHEMIST _EXAMINATION (NEW PATTERN)
EXAMINATION BODY ; UPSC
ELIGIBILITY :_ MSc.Chemistry
UPSC -Conducts annually Geo-chemist Examination , for which number of applicants fill from & probability of final selection is very rare. For this prestigious exam , students work hard & are determinant for sure selection, Keeping this in mind , you need to known very first -that what is required & how to face such a national examination. This blog is an eye opener, just scroll more down to get whole information. Here , we are giving information about Geo-Chemists only:-
Stages of Examination
|
Stage:-1 Preliminary Test (Objective Type ) |
400 Marks |
|
Stage:-2 Mains (Descriptive Type ) |
600 Marks |
|
Stage :-3 Personality Test (Viva **) |
200 Marks |
STAGE :1 OBJECTIVE TEST(PRELIMINARY TEST)
|
STAGE 1: - PRELIMINARY TEST |
MARKS |
DURATION |
|
1. GENERAL STUDIES-I |
100 MARKS |
|
|
2. CHEMISTRY -II |
300 MARKS |
|
SYLLABUS FOR STAGE -1
GENERAL STUDIES :- It covers 7 aspects
Paper-I : General Studies (Common for all streams)
- Current events of national and international importance.
- History of India and Indian National Movement.
- Indian and World Geography -Physical, Social, Economic Geography of India and the World.
- Indian Polity and Governance -Constitution, Political System, Panchayati Raj, Public Policy, Rights Issues, etc.
- Economic and Social Development – Sustainable Development, Poverty, Inclusion, Demographics, Social Sector initiatives, etc.
- General issues on Environmental Ecology, Bio-diversity and Climate Change - that do not require subject specialization
- General Science
Detailed syllabus of chemistry -For Stage -1 ( 300 Marks)
1. Chemical periodicity:
Schrödinger equation for the H-atom. Radial distribution curves for 1s,2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 3d orbitals. Electronic configurations of multi-electron atoms. Periodic table, group trends and periodic trends in physical properties.
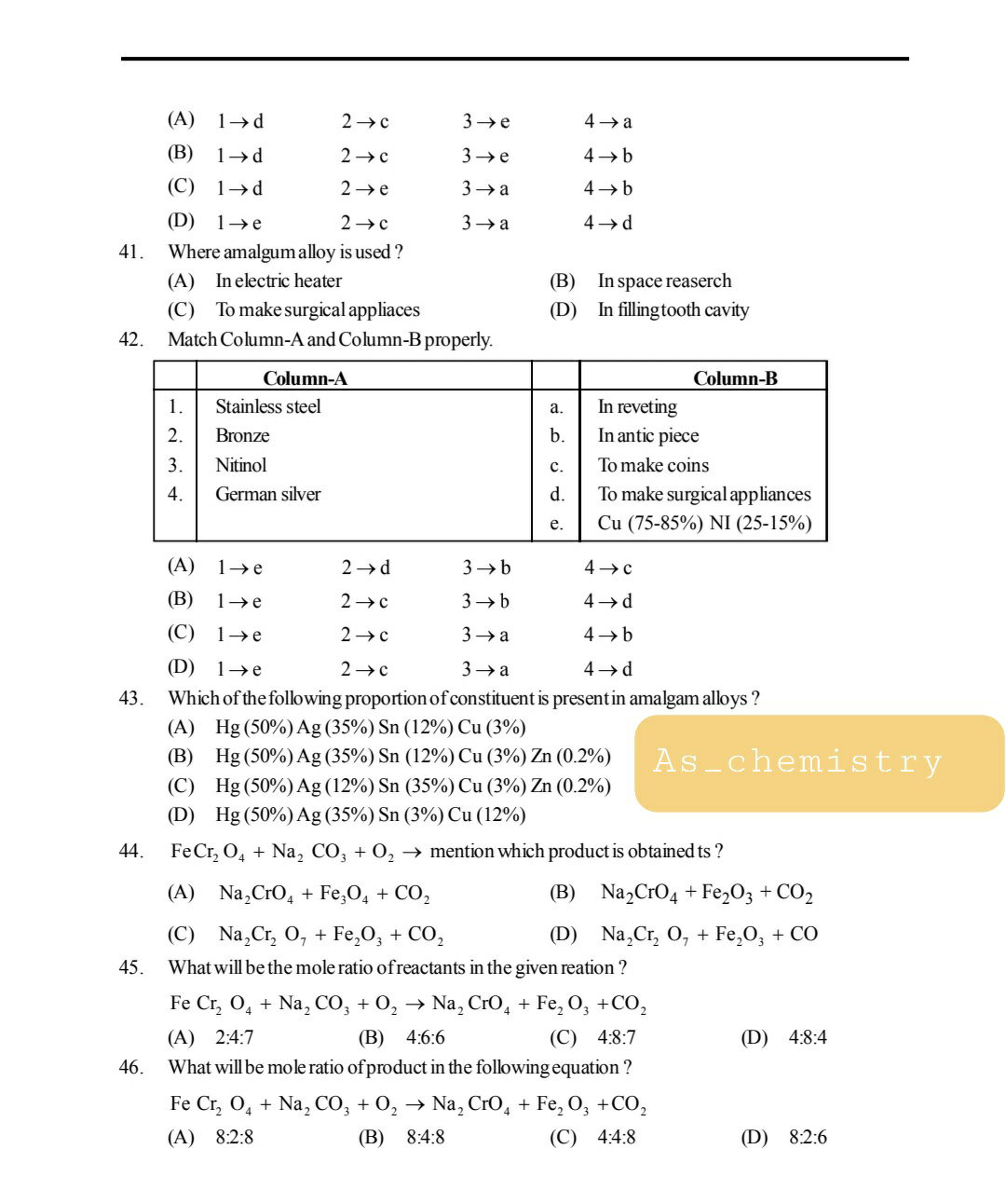
Classification of elements on the basis of electronic configuration. Modern IUPAC Periodic table. General characteristics of s, p, d and f block elements.Effective nuclear charges, screening effects, atomic radii, ionic radii, covalent radii. Ionization enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy and electronegativity. Group trends and periodic trends in these properties in respect of s-, p- and d-block elements. General trends of variation of electronic configuration, elemental forms, metallic nature, magnetic properties, catenation and catalytic properties, oxidation states, aqueous and redox chemistry in common oxidation states, properties and reactions of important compounds such as hydrides, halides, oxides, oxy-acids, complex chemistry in respect of s-block and p-block elements.
BOOKS:-J.D.LEE, 11th NCERT Chemistry
2. Chemical bonding and structure:
Ionic bonding: Size effects, radius ratio rules and their limitations. Packing of ions in crystals, lattice energy, Born-Landé equation and its applications, Born-Haber cycle and its applications. Solvation energy, polarizing power and polarizability, ionic potential, Fajan's rules. Defects in solids. Covalent bonding: Valence Bond Theory, Molecular Orbital Theory, hybridization. Concept of resonance, resonance energy, resonance structures. Coordinate bonding: Werner theory of coordination compounds, double salts and complex salts. Ambidentate and polydentate ligands, chelate complexes. IUPAC nomenclature of coordination compounds. Coordination numbers,
Geometrical isomerism. Stereoisomerism in square planar and octahedral complexes.
BOOKS:- J.D.LEE & 11Th Pardeep's Chemistry
3. Acids and bases:
Chemical and ionic equilibrium. Strengths of acids and bases. Ionization of weak acids and bases in aqueous solutions, application of Ostwald's dilution law, ionization constants, ionic product of water, pH-scale, effect of temperature on pH, buffer solutions and their pH values, buffer action & buffer capacity; different types of buffers and Henderson's equation.
BOOKS :- J.D.LEE & 11th Pardeep Chemistry & 11th NCERT Chemistry
4. Theoretical basis of quantitative inorganic analysis:
Volumetric Analysis: Equivalent weights, different types of solutions, normal and molar solutions. Primary and secondary standard substances. General principles of different types of titrations: i) acid-base, ii) redox, iii)
complexometric, iv) Precipitation. Types of indicators - i) acid-base, ii) redox iii) metal-ion indicators.
BOOK :- Analytical Chemistry -S.Chand
5. Kinetic theory and the gaseous state:
Kinetic theory of gases, average kinetic energy of translation, Boltzmann constant and absolute scale of temperature. Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution of speeds. Calculations of average, root mean square and most probable velocities. Collision diameter; collision number and mean free path; frequency of binary
collisions; wall collision and rate of effusion.
BOOK:- 11th NCERT chemistry , 11th GRB Chemistry -Volume -1
6. Chemical thermodynamics and chemical equilibrium:
First law and its applications to chemical problems. Thermodynamic functions. Total differentials and state functions. Free expansion, JouleThomson coefficient and inversion temperature. Hess’ law. Applications of Second law of thermodynamics. Gibbs function (G) and Helmholtz function (A), Gibbs-Helmholtz equation, criteria for thermodynamic equilibrium and spontaneity of chemical processes.
BOOK;- GRB PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
7. Solutions of non-electrolytes:
Colligative properties of solutions, Raoult's Law, relative lowering of vapour pressure, osmosis and osmotic pressure; elevation of boiling point and depression of freezing point of solvents. Solubility of gases in liquids and solid
solutions.
BOOK :- PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY BY ATUL SINGHAL ( PEARSON PUBLICATION )
8. Electrochemistry:
Cell constant, specific conductance and molar conductance. Kohlrausch's law of independent migration of ions, ion conductance and ionic mobility. Equivalent and molar conductance at infinite dilution. Debye-Hückel theory.
Application of conductance measurements. Conductometric titrations. Determination of transport number by moving boundary method.
BOOK :-Physical chemistry Puri ,sharma & pathania
9. Basic organic chemistry:
Delocalized chemical bond, resonance, conjugation, hyperconjugation, hybridisation, orbital pictures of bonding sp3, sp2, sp: C-C, C-N and C-O system), bond polarization and bond polarizability. Reactive intermediates:
General methods of formation, relative stability and reactivity of carbocations, carbanions and free radicals.
BOOK :- SN SANYAL
10. Stereochemistry:
Configuration and chirality (simple treatment of elements of symmetry), optical isomerism of compounds containing two to three stereogenic centres, R,S nomenclature, geometrical isomerism in compounds containing two C=C double bonds (E,Z naming), and simple cyclic systems, Newman projection (ethane and substituted ethane).
BOOK :- Organic By O.P Tondon
11. Types of organic reactions:-
Aliphatic substitution reactions: SN1, SN2 mechanisms, stereochemistry,relative reactivity in aliphatic substitutions. Effect of substrate structure, attacking nucleophile, leaving group and reaction medium and competitive
reactions. Elimination reactions: E1, E2, mechanisms, stereochemistry, relative reactivity in aliphatic eliminations. Effect of substrate structure, attacking base, leaving group, reaction medium and competitive reactions, orientation of the double bond, Saytzeff and Hoffman rules. Addition reactions: Electrophilic, nucleophilic and radical addition reactions at carbon-carbon double bonds. Electrophilic and nucleophilic aromatic substitution: Electrophilic (halogenation, sulphonation, nitration, Friedal-Crafts alkylation and acylation), nucleophilic (simple SNAr, SN1 and aryne reactions).
BOOK :- Organic By O.P Tondon
12. Molecular Rearrangements:
Acid induced rearrangement and Wagner-Meerwein rearrangements. Neighboring group participation.
BOOKs :- Alluwalia , Jagadamga Singh Yadav
|
NOTE :- BOOKS YOU MUST HAVE
|
|
SUBJECTS _ DESCRIPTIVE TYPE |
MARKS |
DURATION |
|
|
Chemistry -I |
200 Marks |
3 Hours |
|
|
Chemistry -II |
200 Marks |
3 hrs |
|
|
Chemistry-III |
200 Marks |
3 hrs |
|
|
GENERAL ENGLISH ( COMPULSORY FOR ALL ) |
100 Marks |
3 hrs |
|
Chemistry Paper I (200 Marks)
| Chemical periodicity | s-Block Elements |
| Chemical Bonding and structure | p-Block Elements |
| Chemistry of coordination compounds | Chemistry of d- and f- block elements |
| Acid-Base reactions | Organometallic compounds |
| Precipitation and Redox Reactions | Nuclear chemistry |
Chemistry Paper II (200 Marks)
| Kinetic theory and the gaseous state | Application of Second law of thermodynamics |
| Collision of gas molecules, Real gases | Thermodynamics and Equilibrium |
| Thermodynamics | Acids-bases and solvents |
| Liquid State | Solutions of non-electrolytes |
| Solids | Chemical kinetics and catalysis |
| Adsorption and Surface Chemistry | Electrochemistry |
| Photochemistry | Quantum Chemistry |
| Basic principles and application of spectroscopy | UV Spectra |
| PMR Spectra |
Chemistry Paper III (200 Marks)
| Part A- Analytical (100 Marks) | Part B- Organic (100 Marks) |
| Theoretical basis of Quantitative inorganic analysis | Basic organic chemistry |
| Gravimetric Analysis | Organometallic compounds |
| Sampling and treatment of samples for chemical analysis | Bonding and physical properties |
| Acid base titrations | Aldol and related reactions |
| Redox Titrations | Mechanism of some name reactions |
| Potentiometry | Electro cyclic Reactions |
| Complexometric titrations | Organic Reaction Mechanisms |
| Chromatographic methods of analysis | Organic Spectroscopy |
| UV-Visible Spectroscopy | |
| Flame photometry and Atomic absorption spectrometry | |
| X-ray methods of Analysis | |
| Inductively coupled plasma spectroscopy | |
| Analysis of Minerals, Ores and Alloys | |
| Analysis of petroleum and petroleum products | |
| Analysis of coal and coke |
Stage -III
Tuesday, 28 July 2020
Sunday, 26 July 2020
IONS-CATION & ANIONS

CATIONS:-
|
ANIONS
|
||
Suffix – IUM
Na+( Sodium)
K+(Potassium)
Li+(Lithium)
Rubidium(Rb+)
Caesium(Cs+)
H3O+(Hydronium)
Mg2+(Magnesium)
Ca2+(Calcium)
Ba2+(Barium)
Strontium (Sr2+)
Al3+(Aluminium
)
Ga3+(Galium
)
|
Suffix-
OUS
Fe2+(
Ferrous)
Hg+(Mercurous)
Cu+(Cuprous)
Pb2+(Plumbous)
Sn2+(Stannous)
SUFFIX- IC
Ferric (Fe3+)
Mercuric (Hg2+)
Cupric (Cu2+)
Plumbic ( Pb4+)
Stannic ( Sn4+)
|
Suffix –ate
Carbonate – CO32-
Bicarbonate- HCO3-
Nitrate – NO3-
Sulphate- SO42-
Phsophate- PO43-
Borate- BO33-
Suffix – ite
Nitrite – NO2-
Sulphite-SO32-
|
Suffix – ide
Fluoride- F-
Chloride- Cl-
Bromide- Br-
Iodide- I-
Hydroxide- OH-
Oxide- O2-
Sulphide-S2-
Nitride - N3-
Hydride – H-
|
Valency :- The combining power( or capacity) of an element is known as its valency
Valence electrons:- Number of electrons present in the valence shell ( or Outer most shell ) of an atom
Polyatomic ion :- are group of atoms carrying a net charge. They contain more than one type of element -as Phosphate ions- Contains O & P element , Sulphate ion( Contains S & O) , Bicarbonate ion ( Contain H,C& O ) etc
To be Continued .......
Sunday, 5 July 2020
Electrochemical Cell
Electrochemical cell :-
- An electrochemical cell is a device that converts the chemical energy into electrical energy of a spontaneous redox reaction. (Definition )
- Here Gibbs free energy of the spontaneous redox reaction is converted into electrical work which may be used for running a motor or other electrical gadgets like geyser, fan , heater etc
- Electrochemical or Voltaic(galvanic) cells are of a type that produce electric current as a result of chemical reaction
- Apparatus:- Electrochemical cell consists of -Two electrodes usually set up in two separate beakers. The electrolytes taken in the two beakers are different. The electrodes taken are of different materials. To set up this cell , a salt bridge/porous pot is used.
- Sign Convention :- Anode (-ve pole) & cathode(+ve pole)
- Cell Diagram :-
salt Bridge :- Necessity to use salt bridge
- It is a U-shaped tube that contains a gel permeated with a solution of an inert electrolyte such as Sodium sulphate, potassium nitrate or potassium sulphate etc . The ions of the inert electrolyte do not react with the other ions in the solution & they are not oxidised or reduced at the electrodes. The salt-bridge is necessary to complete the electrical circuit & to maintain electrical neutrality in both compartments ( by flow of ions)
Representation of Electrochemical cell
Chemical reaction involved in electrochemical cell
Facts :-
- If the external potential applied becomes greater than internal one then cell behaves as an electrolytic cell & thus the direction of flow of current is reversed
- The potential difference between the two electrodes of a galvanic cell is called cell potential & is measured in Volts.It is called emf of the cell when no current is drawn through the cell.
- For Daniell cell, the cell potential is -1.1V .
- Ecell= Eright - E left
- Measurement of electrode potential is done by using SHE( standard Hydrogen Electrode)
Haloalkanes & Haloarenes II
Haloalkanes & Haloarenes II Part I deals with RX & chloroform Part 2 deals with ArX & Dihalides + Properties of chloroform. ...

-
Haloalkanes & Haloarenes II Part I deals with RX & chloroform Part 2 deals with ArX & Dihalides + Properties of chloroform. ...